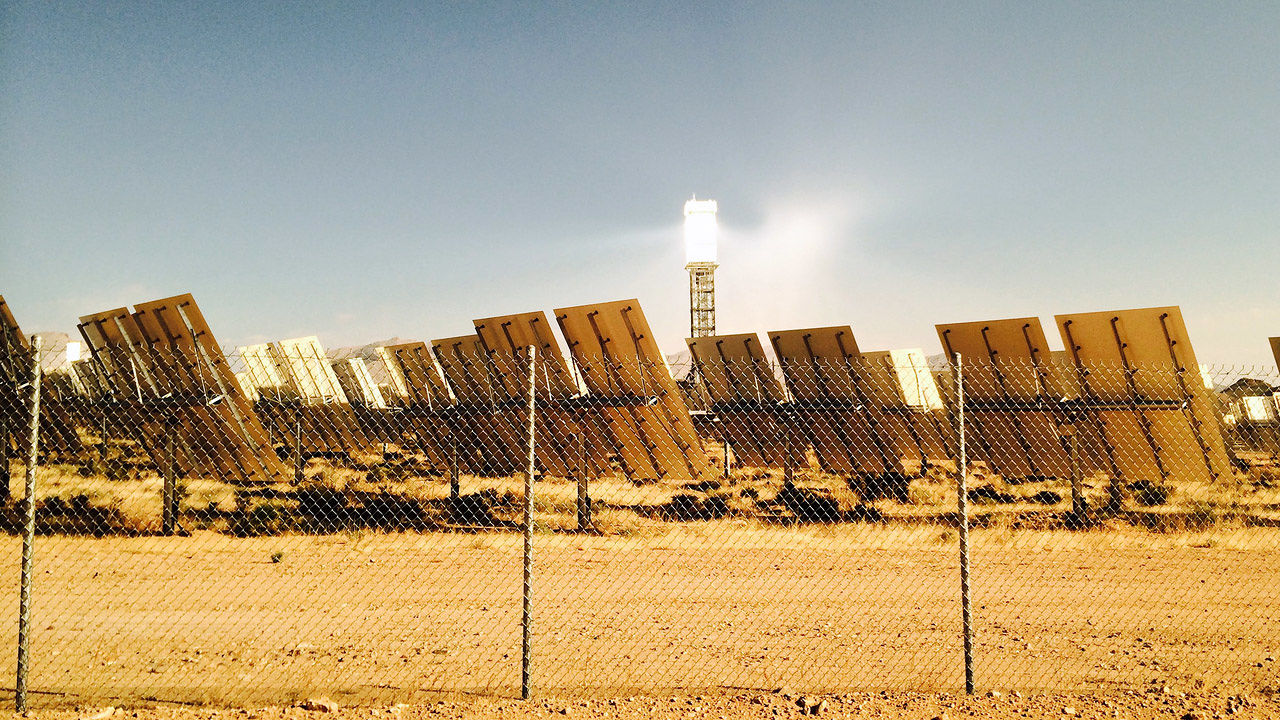
GE Is working on A solution to turn CO2 pollution Into solar Batteries
GE has introduced it’s engaged on a way to make use of CO2 air pollution to make new types of sunlight batteries that might each and every energy up to one hundred,000 houses. CO2 is the main contributor to local weather alternate, and is released into the atmosphere when coal is processed at power vegetation. at the moment environmental strategies imply that some CO2 from these vegetation is captured and saved, so it’s no longer released back into the ambiance. but the query has at all times been: What do you do with the stored fuel?
Now GE says it’s found out a technique to put that saved CO2 to use by using using it as a large battery that could retailer excess solar vitality. The method would additionally get to the bottom of another long-standing energy drawback: the way to retailer solar energy so you should use it when needed most—at nights or on cloudy days. “That’s the grand challenge,” according to Stephen Sanborn, senior engineer at GE global analysis. “We need to make renewable power available to the grid when it is needed.”
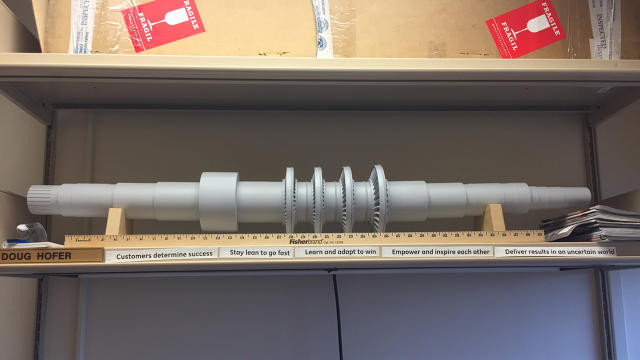
Sanborn’s resolution works in two components. the primary collects solar energy and stores it in a liquid of molten salt. The 2nd part makes use of surplus electrical energy from the power grid to chill liquid CO2 so it turns into dry ice. all through energy generation, the molten salt transforms the dry ice CO2 right into a “supercritical” fluid, that could be a state of matter that neither has particular liquid nor gasoline phases. That supercritical fluid then flows right into a CO2 turbine known as the sunrotor. it is the sunrotor that can then dole out the saved sunlight energy as wanted. Sanborn’s staff has created a model of the sunrotor that is small enough to suit on an place of job shelf, but power one hundred,000 homes.
Sanborn says the sunrotor may convey the cost of power down from $250 per megawatt-hour to $100 per megawatt-hour. “it’s so low cost as a result of you are not making the energy, you take the power from the sun or the turbine exhaust, storing it and transferring it,” he says. as soon as deployed sunrotors could yield as so much as sixty eight% of stored energy again to the facility grid. Even the most efficient fuel power vegetation currently simplest yield 61% of energy again to the grid. As for the timeline of deployment, Sanborn says sunrotors might see standard use within 5 to 10 years.
“the result is a excessive-efficiency, high-efficiency renewable vitality gadget so as to reduce the use of fossil fuels for power generation,” Sanborn says.
fast company , learn Full Story
(24)














