MIT’s not-So-crazy Quest To do away with Stoplights
the first stoplight used to be a complete catastrophe.
put in in London in 1868, the gas-powered traffic sign exploded, killing the policeman who was liable for running it. in the 150 years in view that, the stoplight advanced from a dangerous novelty to a crucial a part of our world. today, there are some 12,460 site visitors indicators in New York city alone. still, some city planners and scientists say the stoplight is nearing the end of its useful lifestyles as city infrastructure—and that its design flaws waste tens of millions of hours of our time unnecessarily.
This week, a crew from MIT published a find out about in the journal PLoS One inspecting a radical thought: do away with the stoplights completely. Led with the aid of Senseable city Lab‘s Carlo Ratti and Paolo Santi of the Ambient Mobility Lab, the paper proposes something known as a “slot-primarily based” intersection, or SI, where cars and infrastructure be in contact via an algorithm that choreographs a sleek dance of auto platoons via an intersection.
Slot-based Design
It appears like madness to start with look, however slot-primarily based community design has already populated other industries. an ideal instance comes from airlines, as Ratti and Santi level out. Take Southwest—instead of letting people line up suddenly to board a aircraft, the airline divides folks into six batches, every of which boards at an explicit time.
the process may irk passengers—especially heart-seat suckers—nevertheless it’s actually amongst the fastest how to board a plane. It’s a form of “slot-based” scheduling, which is already in use everywhere from air traffic keep watch over to industry management. the elemental thought is that actors in a gadget are grouped into batches, and the rate of their motion is thoroughly managed to move them extra efficiently through a space.
It’s known as the “slower-is-faster impact,” as Santi and Ratti give an explanation for, mentioning that whereas slot-based design has regarded in different industries, it hasn’t arrived in site visitors design but. they believe that time has come, and in their paper, they show how it could double the efficiency of intersections and reduce delays “to almost zero.”
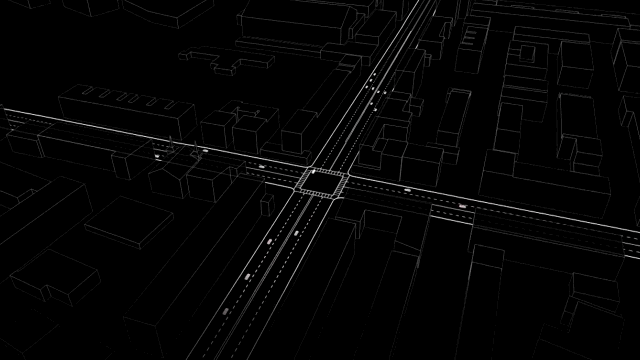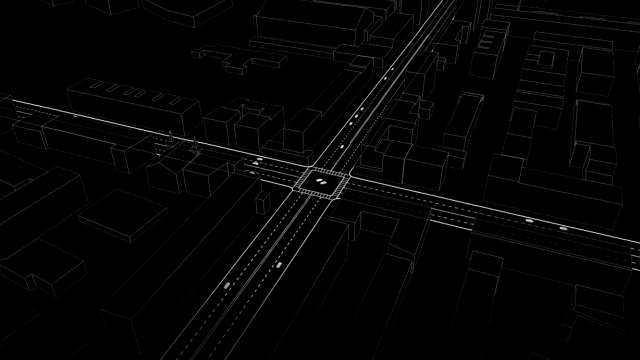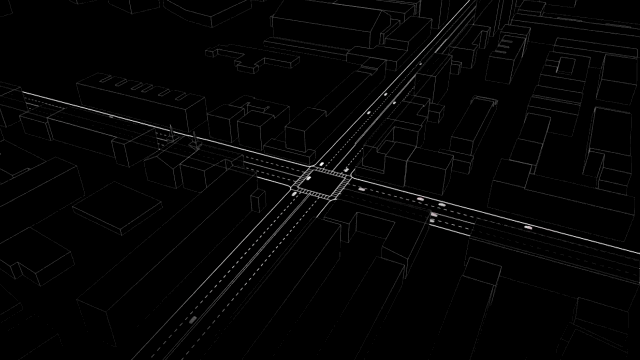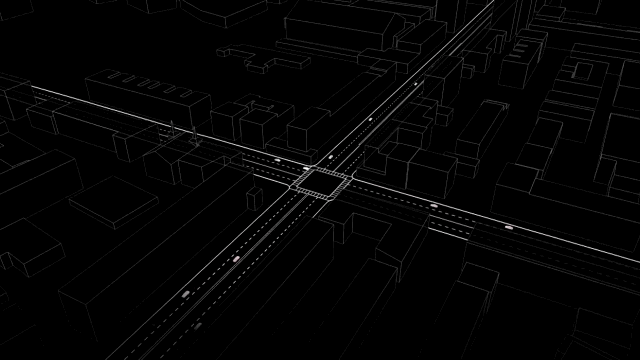
What would their device appear to be in practice? As Santi explains, a slot-based totally intersection would depend on two things. First, a sensor-geared up automobile would want to keep up a correspondence its trajectory—right, left, or straight—to a relevant algorithm controlling the intersection, which might crew it right into a “batch” of alternative cars stepping into the identical direction. 2d, the central tool gadget would need to be able to keep watch over the velocity of every platoon, the use of cruise regulate-model device that already exists in most cars, to restrict the velocity of your automotive because it moved throughout the intersection.
whereas the MIT team says this method can be at its best with totally self reliant vehicles, it’s feasible with today’s auto tech, too. “on the subject of what kind of expertise you may need, you gained’t need to wait twenty years,” Santi says. “We don’t need autonomous driving. It’s in fact so much simpler.”

whereas the paper does not delve deeply into the technical important points of the machine, the hardware sounds much like the Connective automobile Pilot program at present being tested by the department of Transportation. it might probably work something like this: imagine you’re using residence, heading into the busy intersection close to your home that’s at all times snarled with traffic. when you sign a left flip, your car’s onboard computer sends a ping to the significant community controlling the intersection. The device responds with the optimal speed for your automobile to commute in keeping with your trajectory—and your automotive’s device sets a limit on how fast that you can go based on that number, not in contrast to cruise keep an eye on. You subscribe to a platoon of alternative vehicles turning left, and this batch of vehicles gently arcs in the course of the intersection, whereas other platoons heading totally different directions both velocity up or decelerate to accommodate it.
the problem With Yellow
the issue isn’t that stoplights are poorly designed—it’s that there’s an extraordinarily tangible limit to how efficient they are able to be. It’s all concerning the yellow gentle.
The earliest stoplights didn’t have yellow, as a result of they didn’t want it: These primitive methods had been controlled a police officer sitting in a booth local. in the Twenties, a Detroit policeman named William Potts got here up with the idea of an “amber” gentle that will alert drivers that the light was about to vary. In turn, this eliminated the necessity for a human operator as a result of it communicated everything a driver wanted to grasp routinely.

It was a brilliant design, but it surely’s additionally subject to diminishing returns. you can increase the number of light adjustments at an intersection and greatly speed up the drift of site visitors, the authors write. however with every trade, you add another “setup” section, aka a yellow light, which decreases total efficiency on the intersection.
What Santi and Ratti are proposing is an ideal-intelligent piece of software that could take the fundamental version of a stoplight—biking between cease and go—and pace it up, lowering the wasted time of yellow lights and increasing the choice of vehicles that may transfer via an intersection, while it slows them down to raised coordinate their movements. it would dissolve our thought of the stop-and-go site visitors machine by means of adapting to the wishes of a community in actual time, they provide an explanation for. The computational prognosis of their version printed that it could possibly make gentle-free intersections twice as environment friendly as conventional ones.
the largest problem of adopting a slot-based totally visitors design will not be with the statistical modeling or technology in the back of it—it could be with the human habits sitting behind the wheel. “of course, giving up keep watch over is something that’s very troublesome for humans,” Santi says.

To deal with the momentous cultural shift that a slot-based totally site visitors device would require us to make, he envisions an incremental trying out strategy, equipping a small area of a metropolis with the device, no longer in contrast to the best way other researchers are checking out similar ideas, reminiscent of this four-block-lengthy a part of Chicago that is gone utterly free of lights, sidewalks, and curbs. the idea that may be tested in vehicles which can be already running semi-autonomously within a closed area or campus. it could even be utilized to bikes or walkers who’re looking to pass busy intersections. For now, the MIT group is in talks with a couple of cities to apply the theory, though they are able to’t disclose where.
“From a technological standpoint, there are no large hurdles to enforce this concept,” Santi says. the true hurdle is also within the radical behavioral shift so as to be required on the a part of drivers. simply as the in style adoption of self reliant automobiles has run up against unpredictable drivers, the most important enemy of independent intersections is also people.
(35)













