the most recent leap forward In figuring out Diabetes used to be Made by An Algorithm
Researchers now consider there are three different varieties of sort 2 diabetes—a end result revealed with lend a hand from machines combing via reams of clinical information.
November 24, 2015
With the fee to sequence a human genome dropping via the day and scientific records ultimately going digital, public well being experts are excited for a new technology of customized, or “precision,” drugs—a tremendous information future wherein there’s no “average” patient, only particular person sufferers with unique genes, environments, and lifestyles. As a measure of this pleasure, this yr, President Obama launched a $215 million initiative with the intention to create a health database from 1 million volunteers that’s unprecedented intimately. Breakthroughs in prevention, figuring out, and therapy of illness are hoped.
although there’s each hype and numerous genuine promise, the sector of precision drugs remains to be in its nascency. Genetic sequencing has helped in the analysis and treatment of uncommon genetic disease and is beginning to be vital within the remedy of some cancers, comparable to lung cancer or brain tumors.
Now a latest study, printed in the journal Science Translational medication, demonstrates the broader promise of precision medicine beyond genome sequencing—and in figuring out an especially widespread illness: kind 2 diabetes.
nearly 1 in 10 american citizens have kind 2 diabetes, and plenty of extra are at risk. yet it’s a poorly understood disease: Its motives, symptoms, and complications are diverse and hard for doctors to foretell. with the aid of mining a database of medical and genetic data from greater than 2,500 diabetes patients, researchers Icahn faculty of medication at Mount Sinai scientific center have now in fact identified some patterns that a whole container of medical doctors have no longer: They discovered there are actually three assorted sub-varieties of kind 2, every of which have very different well being implications.
“that is the first tangible demonstration of precision medicine that may be applied to a more well-liked, advanced disease,” says find out about creator Joel Dudley, director of biomedical informatics at Mount Sinai (and one of fast company’s Most inventive people of 2014), a big clinic in upper new york.
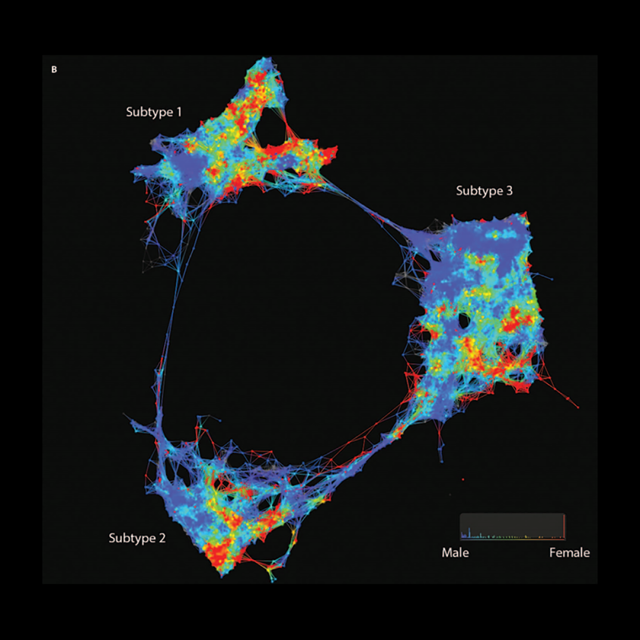
They were in a position to try this with get entry to to a nonetheless rather uncommon assortment of lots of Mount Sinai patients who volunteered to offer their well being charts and genetic data to the hospital for researcher efforts (See “within the hospital Of the long run, giant data Is Your physician“). regularly, doctors just take a look at a couple of blood tests—comparable to blood sugar and insulin ranges—when monitoring diabetes patients. as a substitute, the researchers used pc modeling to map how equivalent each and every affected person was once to one another (a “affected person-affected person similarity network”), in accordance with every bit of well being data—top, weight, blood platelet counts, and hundreds of knowledge points that human medical doctors on my own might by no means process. the result used to be the map, seen above, that displays Mount Sinai patients map into three distinct clusters, or “sub-varieties.”
the larger question, after all, is: Do these sub-varieties topic for a affected person’s health? The find out about found that they most definitely do. patients in a single subtype have been extra prone to endure from most cancers and cardiovascular disease; in every other subtype, they had been at higher possibility for kidney illness and eye issues; finally, within the third sub-sort, hypersensitive reactions, neurological ailments and HIV infections were bigger issues. even more importantly, when the researchers mapped sufferers’ genomes onto the community—they discovered distinctive gene editions related to every sub-team which helped explain one of the variations between them.
“the fact that these genetic components matched up so effectively with the medical factors means that there’s exact biology underlying the variations between these sufferers,” says Dudley, versus other explanations (like way of life selections.)
Diabetes consultants weren’t too shocked by using the patterns in kind 2 diabetes, in step with Dudley—they already knew them of their intestine and had seen sufferers of each “sub-type.” “but they didn’t be able to visualize it in this means,” Dudley says.
the next step might be to duplicate the find out about in other patient populations past upper long island’s distinctive mixture of wealth upper East aspect residents and lower-earnings minority residents of East Harlem. a bigger, long-time period goal is to do a more proactive find out about—to peer if, in keeping with their genes, the unique dangers faced by newly-diagnosed diabetes sufferers will also be estimated and in some way if their treatment plans may also be customized.
ultimately, Dudley envisions transferring these related how one can a number of alternative diseases to make discoveries that weren’t conceivable unless you’re looking at tens of millions of knowledge points immediately. He envisions a “google maps” for a illness like diabetes, the place well being exams would convey the place any given patient was on a broad vary of potentialities for the way the illness would development. however this can be slow—for now, now not many kinds of information units just like the Mount Sinai one exist. The White home initiative will have to add at one essential one.
[top picture: munalin by means of Shutterstock]
quick company , read Full Story
(23)