Google Debuts New PhotoScan App
Google’s new PhotoScan app makes it easy to digitize old prints
Google Photos is also getting a host of more advanced image-editing tools.
Nathan Ingraham , November 15, 2016
On the surface, Google Photos has a simple mission: to store all your pictures. Specifically, Google says it wants the service to be a home for all of your photos, and today that mission expanded to encompass the old photos you took on a point-and-shoot back in the ’90s. The company just released an app called PhotoScan for iOS and Android, and it promises to make preserving the memories in your old printed photos much easier. Additionally, while Google was at it, it also issued several updates to its core Photos app.
PhotoScan is definitely the star of the show, though. According to engineers from Google who showed the app to the press today, PhotoScan improves on the old “photo of a photo” technique that many now use to quickly get a digital copy of old prints. It’s also a lot cheaper than sending pictures out to be scanned by a professional, not to mention faster and more convenient than using a flatbed scanner.
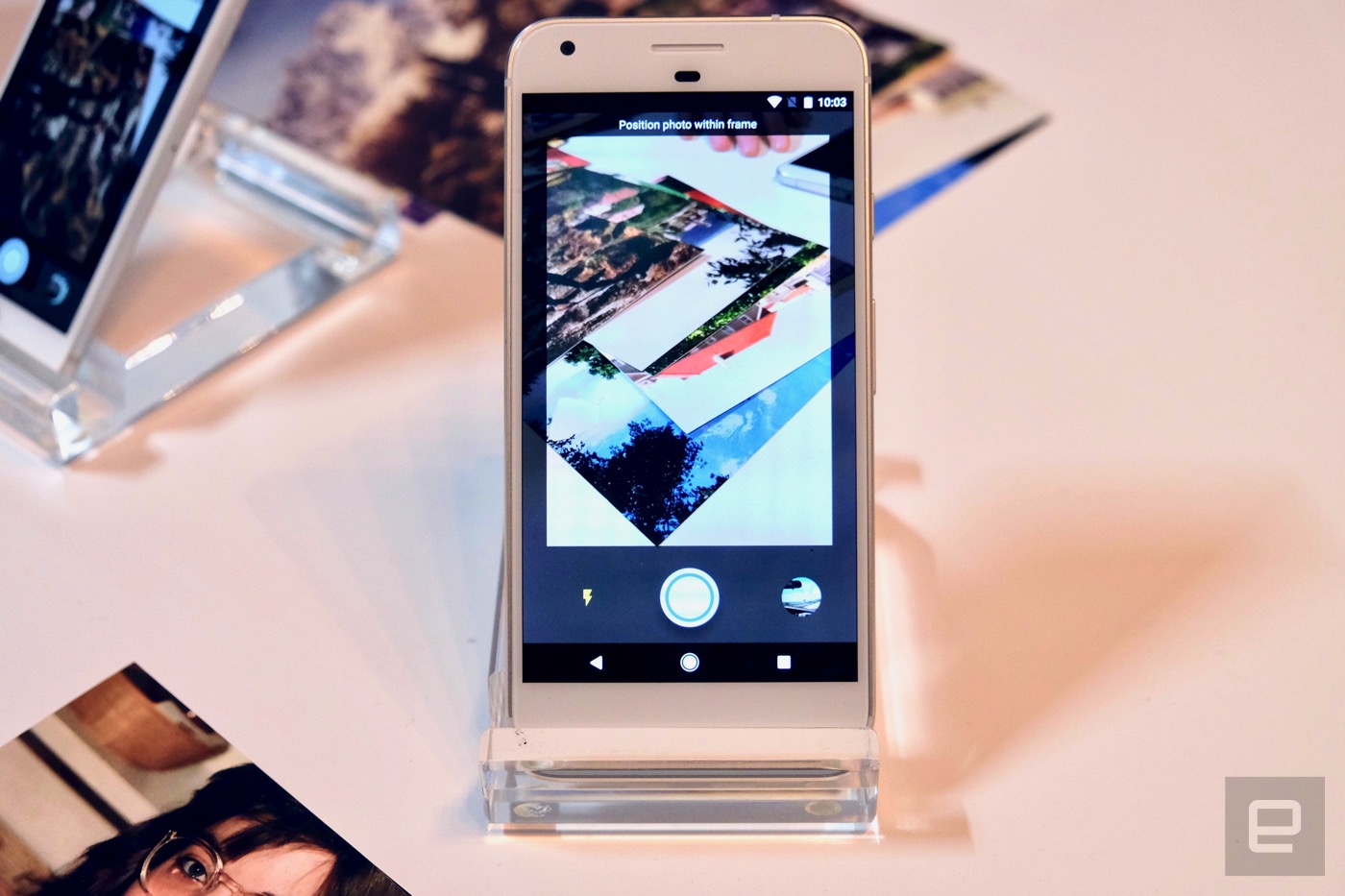
When you open up the PhotoScan app, you’re prompted to line up your picture within a border. Once you have the picture aligned, pressing the scan button will activate your phone’s flash and start the process of getting a high-quality representation of the photo. Four white circles will appear in different quadrants of the image. You’ll be prompted to move your phone over each dot until it turns blue; once all four dots are scanned, the app pulls together the final image.

When moving the phone to scan each dot, the app is taking multiple images of the picture from different angles to effectively eliminate light glare — something Google cited as the biggest culprit in ruining digital pictures of photo prints. In practice, in Google’s tightly controlled demo setup, it worked perfectly. It was easy to see how the lights in the room cast glare on the photo print and equally obvious how the app managed to eliminate it in the final scan. It’s a bit of an abstract process to describe, but it worked as promised. We’ll need to test it further outside of Google’s own testbed, but the early results are definitely encouraging.
The app also lets you adjust the crop to remove any hint of the background surface peeking into the photo, but it’s otherwise a pretty minimal experience. Once you’re done scanning, the app prompts you to save your scans. They’re saved directly to your phone’s storage; you can then upload them to Google Photos or the backup service of your choice. Google specifically said that it wanted this app to exist outside Google Photos so people could scan images and use whatever service they want to back them up.
Beyond PhotoScan are some noteworthy additions to the proper Google Photos app. The biggest change here is that there are a host of new photo-editing options on board. The Google+ app actually used to have a pretty robust set of editing options, but when Photos was liberated as a standalone app, the editing features were significantly culled.
If you want to make further adjustments, the simple “light,” “color” and “pop” sliders that were in the previous Google Photos app have been greatly expanded. Now, you can tap a triangle next to “light” or “color” to see a view with a host of more granular editing tools like exposure, contrast highlights, saturation, warmth and so on. Those tools aren’t right in your face, so people who don’t want to dive in can still make adjustments — but those who really want to go deep on editing their pictures will surely appreciate the option. I used to be a big fan of the Google+ photo-editing tools, so seeing these features come back is very welcome.
Google called out two of those adjustments, in particular, as things that only it can do with its vast store of photographic information. A slider called “deep blue” saturates blues in an image like the sky or water to make them more vibrant, and it knows to specifically target those hues while leaving others unchanged. There’s also a skin-tone filter that can adjust saturation specifically on a subject’s skin without altering the rest of the image. Other editing programs have similar filters, but Google says this one is particularly accurate because of the millions of photos it has analyzed — it just has a better sense of what is skin is, compared with other editors.
Lastly, Google added 12 new filters (of course it did) that take advantage of machine learning to be a little smarter than the standard option. Rather than always slapping a default set of adjustments on a picture, Google Photos will make subtle improvements to the image first; it sounds like a combination of auto enhance as well as a filter. But those enhancements will be optimized to work well with the filter you’re adding. It sounds nice, and the filters looked good on the images Google was showing off, but we’ll need to spend some time playing around with it to see if they’re really any better than what Instagram already offers.
Editing is the main addition to Google Photos, but there are a few other improvements here as well. If you’re invited to a shared an album, the app will prompt you with suggestions from your own photos to add. It’s another place where Google’s machine learning comes into play. And the moviemaker, which can automatically select related photos and set them to a soundtrack, will gain some new event-focused options in the coming months.
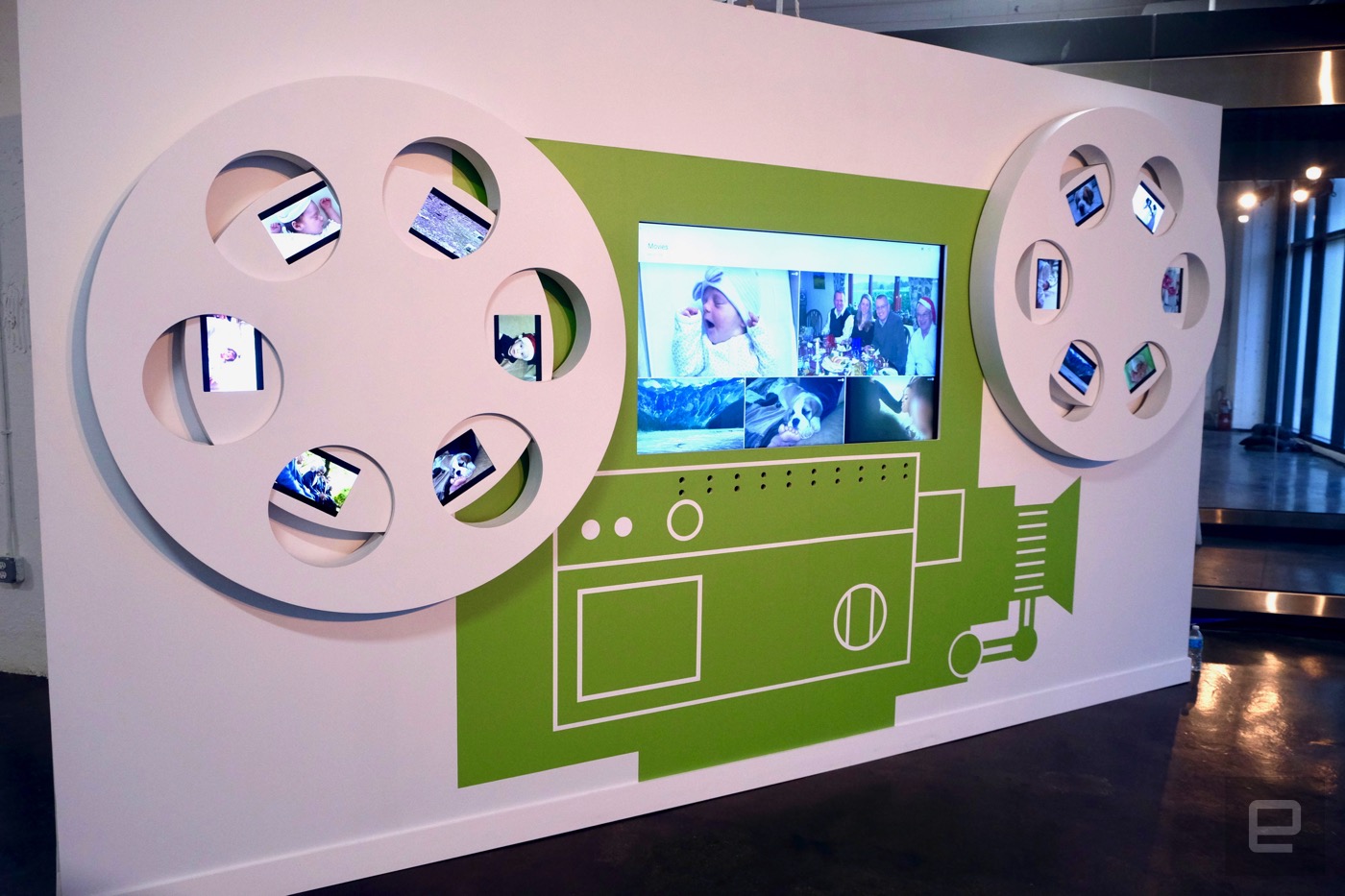

The first of those is “lullaby,” a video made by specifically looking for sleeping-baby photos and combining those with a peaceful soundtrack. Specifically, Google’s servers can find groups of pictures of the same child and look for ones when it is sleeping and pull those all together. Google said it went for the sleeping baby specifically as a way to assemble some calming memories for parents, who always seem to cherish those fleeting moments when their new baby is asleep.
For those of us without kids, Google has a new Christmas memories movie that’ll look at your pictures over the years and pull together ones with Christmas “markers” — things like trees, Santa hats, presents and so forth. In April next year, Google will also start auto-creating movies of pets as well as outdoor moments (timed to launch around Earth Day).
All told, this is probably the biggest update to Google’s photo products since it launched in mid-2015. There are plenty of other services that offer near-unlimited photo backups, but Google’s machine-learning based on all the data in its systems is second-to-none. Yes, that requires Google to analyze everything you put into it, but that’s been the case for years now. If you’re comfortable giving Google access to your data, these photos updates are definitely worth checking out. And if you want to try PhotoScan but are worried about your privacy, you don’t even need to upload your pictures to Google. The new PhotoScan app and updated Google Photos should be available in the App Store and on Google Play now.
(39)