This cute little robot floats to oil spills and sucks up the oil
A decade after a BP drilling rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, sending an estimated 168 million gallons of oil gushing into the water over the course of months, local wildlife are still struggling to recover. Many of the people who worked to clean up the spill are still experiencing health effects. At the time, the “cleanup” strategy involved setting oil slicks on fire and spraying mass quantities of a chemical meant to disperse it, both of which helped get rid of the oil, but also worsened pollution.
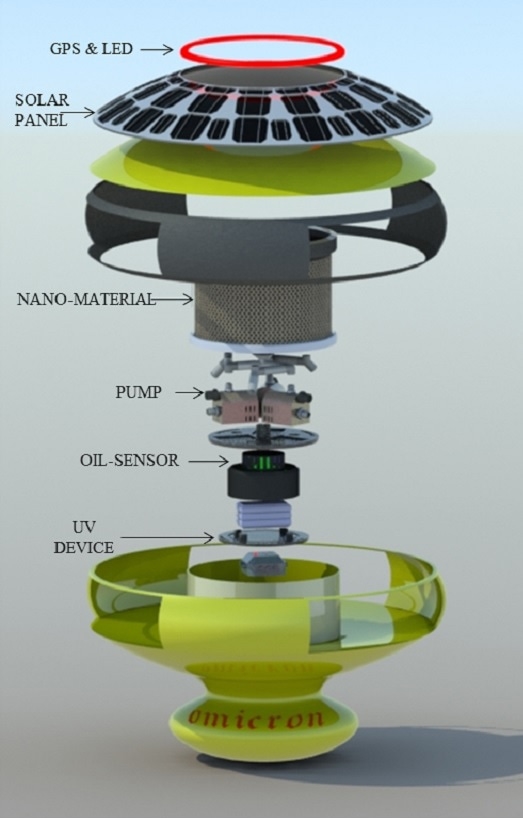
A new robot designed to clean oil spills, now in development, demonstrates how future spills could be handled differently. The robot navigates autonomously on the ocean surface, running on solar power. When oil sensors on the device detect a spill, it triggers a pump that pushes oil and water inside, where a custom nanomaterial sucks up the oil and releases clean water.
“The material repels water and attracts oil,” says Tejas Sanjay Kabra, a graduate student at North Carolina State University who has been developing the technology, called Soilios, over several years. While some other nanomaterials are now in use in oil spills, the new material is unique in that it’s made from leaves rather than fossil fuels. And while current processes still involve burning oil at the site of the spill, the new material can recover the oil. The robot, which is an entry in the 2020 James Dyson Award competition, can go out, collect the oil, and come back, and then the oil would be removed from the sponge-like material, which can be reused as many as 180 times.
Kabra 3D-printed a small prototype of the robot, which he tested in a lab, a swimming pool, and then the open ocean. (The small version, about two feet across, can collect 20 gallons of oil at a time; the same device can be scaled up to much larger sizes). He now hopes to bring the product to market as quickly as possible, as major oil spills continue to occur—such as the spill in Russia in June that sent more than 20,000 metric tons of diesel into a pristine part of the Arctic.
(67)



